思路 二分查找
把问题转换为找两个数组中第k大的数,当n+m为奇数,中位数是两个数组中第$(m+n+1)/2$个元素,当n+m为偶数,中位数是第$(m+n)/2$和$(m+n)/2+1$个数的平均数。
实现比较恶心,每个数组分别定义一个偏移量offs1和offs2,令mid1=offs1+k/2-1,mid2=offs2+k/2-1每次比较a[mid1]和b[mid2],根据上面的思路,a[mid1]>=b[mid2]那mid1及以前的数字都可被排除了,偏移量offset1+=k/2(因为包括a[mid1]所以是k/2-1+1)。因为现在已经排除了k/2个数字,k-=k/2。反之亦然。
现在还有一个需要考虑的就是边界情况,有可能offs1+k/2-1已经超过数组范围,所以要和数组长度n取一个min,同理在更新offs1和k的时候也要取min,因为如果mid1超过数组范围的话可以排除的数的个数就不是k/2个,而是n个。我们知道当k==1时答案就是此时a[offs1],b[offs2]的最小值。因为到这一步意味着我们已经排除了k-1个数字,只差最后一个就能找到第k大的元素。但如果k还没到1就有一边数组超出边界了呢?如果a数组二分到头了,那就直接返回b[offs2+k-1]就是答案了。考虑a数组为空的情况,offs2=0,就相当于直接找b[k-1](下标从0开始)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public : int n,m; int check (int k,vector<int >& nums1, vector<int >& nums2) int offs1=0 ,offs2=0 ; int mid1,mid2; while (true ){ if (offs1>=n)return nums2[offs2+k-1 ]; if (offs2>=m)return nums1[offs1+k-1 ]; if (k==1 )return min (nums1[offs1],nums2[offs2]); mid1=min (offs1+k/2 -1 ,n-1 ),mid2=min (offs2+k/2 -1 ,m-1 ); if (nums1[mid1]<=nums2[mid2]){ offs1+=min (k/2 ,n); k=k-min (k/2 ,n); } else { offs2+=min (k/2 ,m); k=k-min (k/2 ,m); } } } double findMedianSortedArrays (vector<int >& nums1, vector<int >& nums2) int ans,k; n=nums1.size (),m=nums2.size (); if ((n+m)%2 ==1 ){ return check ((n+m+1 )/2 ,nums1,nums2); } else { return (double (check ((n+m)/2 ,nums1,nums2))+double (check ((n+m)/2 +1 ,nums1,nums2)))/2.0 ; } return double (ans); } };
思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public : bool judge (char a,char b) if (a==b||b=='.' )return true ; return false ; } bool isMatch (string s, string p) bool dp[105 ][105 ]={false }; int n=s.length (),m=p.length (); dp[0 ][0 ]=true ; s=" " +s,p=" " +p; for (int i=0 ;i<=n;i++){ for (int j=1 ;j<=m;j++){ if (j+1 <=m&&p[j+1 ]=='*' )continue ; if (i&&p[j]!='*' ){ dp[i][j]=dp[i-1 ][j-1 ]&&judge (s[i],p[j]); } else if (p[j]=='*' ){ dp[i][j]=dp[i][j-2 ]||i&&dp[i-1 ][j]&&judge (s[i],p[j-1 ]); } } } return dp[n][m]; } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public : int maxArea (vector<int >& h) int len=h.size (); int l=0 ,r=len-1 ; int ans=0 ; while (l<=r){ ans=max (ans,(r-l)*min (h[l],h[r])); if (h[l]<=h[r]){ l++; } else r--; } return ans; } };
思路 dfs 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public : vector<string>v; void dfs (string path,int l,int r,int n) if (l>n||r>n||r>l)return ; if (l==n&&r==n){ v.push_back (path); } dfs (path+'(' ,l+1 ,r,n); dfs (path+')' ,l,r+1 ,n); } vector<string> generateParenthesis (int n) { dfs ("" ,0 ,0 ,n); return v; } };
dp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public : vector<string> generateParenthesis (int n) { if (n == 0 ) return {}; if (n == 1 ) return { "()" }; vector<vector<string>> dp (n+1 ); dp[0 ] = { "" }; dp[1 ] = { "()" }; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j <i; j++) { for (string p : dp[j]) for (string q : dp[i - j - 1 ]) { string str = "(" + p + ")" + q; dp[i].push_back (str); } } } return dp[n]; } };
思路
栈里面存的是最后一个没有被匹配的括号的下标。
如果是’(‘直接入栈。
是’)’如果栈内有元素就将栈顶弹出。弹出后栈空了说明该右括号失配
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public : int longestValidParentheses (string s) stack<int >st; int ans=0 ; st.push (-1 ); for (int i=0 ;i<s.length ();i++){ if (s[i]=='(' )st.push (i); else { st.pop (); if (st.empty ()){ st.push (i); } ans=max (ans,i-st.top ()); } } return ans; } };
思路 双指针 左指针和右指针分别从两端开始,维护一个lmax和rmax,分别代表左右两边当前的最高高度。注意如果$h[l]<h[r]$移动左指针。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public : int trap (vector<int >& h) int len=h.size (); int l=0 ,r=len-1 ; int lmax=0 ,rmax=0 ; int ans=0 ; while (l<=r){ if (h[l]<=h[r]){ if (lmax>h[l])ans+=lmax-h[l]; lmax=max (lmax,h[l]); l++; } else { if (rmax>h[r])ans+=rmax-h[r]; rmax=max (rmax,h[r]); r--; } } return ans; } };
单调栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public : int trap (vector<int >& h) int len=h.size (); stack<int >st; int ans=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<len;i++){ while (st.size ()>=2 &&h[i]>h[st.top ()]){ int t=st.top (); st.pop (); int l=st.top (); ans+=(i-l-1 )*max (0 ,(min (h[i],h[l])-h[t])); } st.push (i); } return ans; } };
思路 螺旋矩阵2改一改,考虑一下行列不同的情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution {public : vector<int > spiralOrder (vector <vector<int >> &a) { int cnt = 1 ; int n=a.size (); int m=a[0 ].size (); int N=n,M=m; n--; m--; vector <int > v; int c = 0 ; while (cnt <= N * M) { for (int i = c; i <= m; i++) { v.push_back (a[c][i]); cnt++; } if (cnt > N * M)break ; for (int i = c + 1 ; i <= n; i++) { v.push_back (a[i][m]); cnt++; } if (cnt > N * M)break ; for (int i = m - 1 ; i >= c; i--) { v.push_back (a[n][i]); cnt++; } if (cnt > N * M)break ; for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= c + 1 ; i--) { v.push_back (a[i][c]); cnt++; } c++; m--; n--; } return v; } };
思路 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public : vector<vector<int >> generateMatrix (int n) { int cnt=1 ; vector<vector<int >>a (n, vector <int >(n)); int c=0 ,l=n-1 ; while (cnt<=n*n){ for (int i=c;i<=l;i++){ a[c][i]=cnt; cnt++; } for (int i=c+1 ;i<=l;i++){ a[i][l]=cnt; cnt++; } for (int i=l-1 ;i>=c;i--){ a[l][i]=cnt; cnt++; } for (int i=l-1 ;i>=c+1 ;i--){ a[i][c]=cnt; cnt++; } c++; l--; } return a; } };
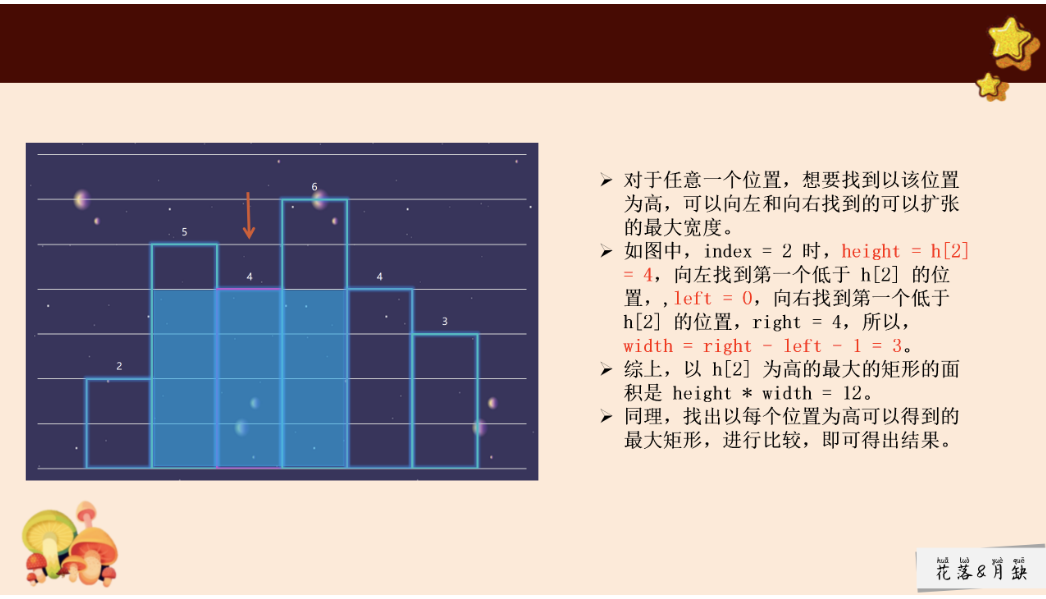
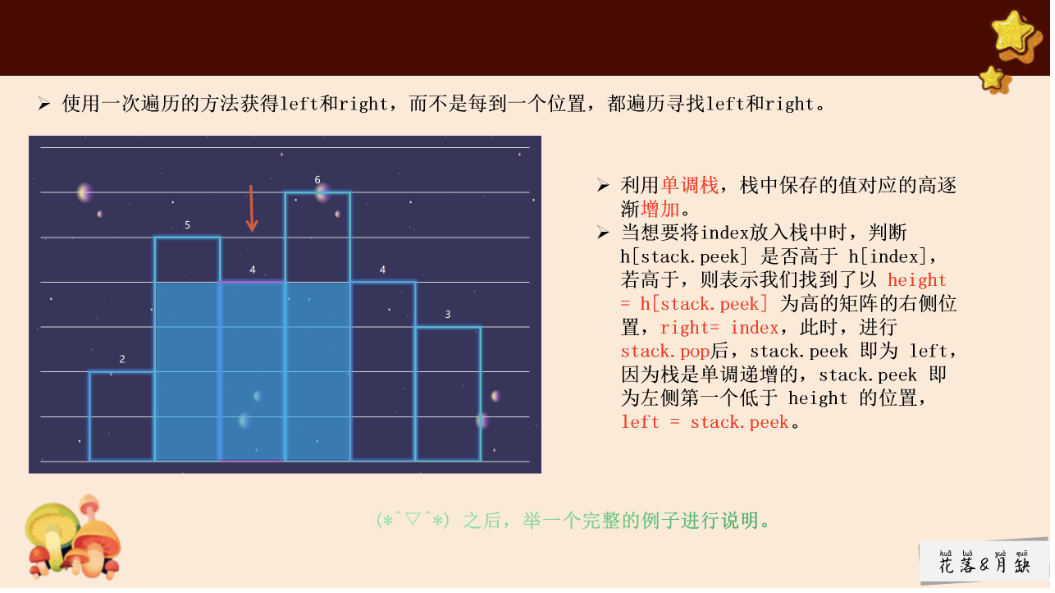
思路
详细解释:https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/solutions/142012/bao-li-jie-fa-zhan-by-liweiwei1419/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {public : int largestRectangleArea (vector<int >& heights) stack<int >st; st.push (-1 ); int n=heights.size (); int ans=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ while (st.top ()!=-1 &&heights[i]<heights[st.top ()]){ int h=heights[st.top ()]; st.pop (); while (st.top ()!=-1 &&heights[st.top ()]>=h){ st.pop (); } int w=i-st.top ()-1 ; ans=max (ans,h*w); } st.push (i); } while (st.top ()!=-1 ){ int h=heights[st.top ()]; st.pop (); while (st.top ()!=-1 &&heights[st.top ()]>=h){ st.pop (); } int w=n-st.top ()-1 ; ans=max (ans,h*w); } return ans; } };
思路 给定一个heights[i][j]记录第j列连续的1的个数
1 2 3 4 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 --> 2 0 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 --> 3 1 3 2 2 1 0 0 1 0 4 0 0 3 0
有了heights[i][j]后就相当于对每一层i求柱状图中最大的矩形(上一题)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution {public : int maximalRectangle (vector<vector<char >>& matrix) int heights[205 ][205 ]={0 }; int m=matrix.size (); int n=matrix[0 ].size (); stack<int >st; st.push (-1 ); int ans=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ if (matrix[i][j]=='1' ){ if (i>0 ){ if (heights[i-1 ][j])heights[i][j]=heights[i-1 ][j]+1 ; else heights[i][j]=1 ; } else heights[i][j]=1 ; } } cout<<'\n' ; for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ while (st.top ()!=-1 &&heights[i][j]<heights[i][st.top ()]){ int h=heights[i][st.top ()]; st.pop (); while (st.top ()!=-1 &&heights[i][st.top ()]>=h){ st.pop (); } int w=j-st.top ()-1 ; ans=max (ans,h*w); } st.push (j); } while (st.top ()!=-1 ){ int h=heights[i][st.top ()]; st.pop (); while (st.top ()!=-1 &&heights[i][st.top ()]>=h){ st.pop (); } int w=n-st.top ()-1 ; ans=max (ans,h*w); } } return ans; } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {public : void merge (vector<int >& nums1, int m, vector<int >& nums2, int n) int i=m-1 ; int j=n-1 ; int idx=m+n-1 ; if (m==0 )nums1=nums2; while (idx>=0 ){ if (i>=0 &&j>=0 ){ if (nums1[i]<=nums2[j]){ nums1[idx]=nums2[j]; idx--; j--; } else { nums1[idx]=nums1[i]; nums1[i]=0 ; idx--; i--; } } else if (i<0 ){ nums1[idx]=nums2[j]; j--; idx--; } else if (j<0 ){ nums1[idx]=nums1[i]; i--; idx--; } } } };
思路 对于这颗二叉树,可能的路径情况有
b + a + c
b + a + a 的父结点
a + c + a 的父结点
把b节点思考成一坨左子树,c节点思考成一坨右子树。
如果b整体比0小那直接不用选了,c同理。
考虑从小往上递归。对于每一个节点,他都有可能作为一个”转折点”,或者作为一个单边继续向上递归。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public : int maxx=INT_MIN; int dfs (TreeNode* u) if (u==nullptr )return 0 ; int l=max (0 ,dfs (u->left)); int r=max (0 ,dfs (u->right)); maxx=max (maxx,u->val+l+r); return u->val+max (l,r); } int maxPathSum (TreeNode* root) dfs (root); return maxx; } };
思路 dfs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {public : vector<vector<int >>ans; vector<int >path; void dfs (TreeNode *root,int sum) if (root==nullptr )return ; sum-=root->val; path.push_back (root->val); if (root->left==nullptr &&root->right==nullptr &&sum==0 ){ ans.push_back (path); } dfs (root->left,sum); dfs (root->right,sum); sum+=root->val; path.pop_back (); } vector<vector<int >> pathTarget (TreeNode* root, int target) { dfs (root,target); return ans; } };
思路 对于这颗二叉树,可能的路径情况有
b + a + c
b + a + a 的父结点
a + c + a 的父结点
把b节点思考成一坨左子树,c节点思考成一坨右子树。
如果b整体比0小那直接不用选了,c同理。
考虑从小往上递归。对于每一个节点,他都有可能作为一个”转折点”,或者作为一个单边继续向上递归。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public : int maxx=INT_MIN; int dfs (TreeNode* u) if (u==nullptr )return 0 ; int l=max (0 ,dfs (u->left)); int r=max (0 ,dfs (u->right)); maxx=max (maxx,u->val+l+r); return u->val+max (l,r); } int maxPathSum (TreeNode* root) dfs (root); return maxx; } };
思路 用到了后序遍历的特点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public : TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { if (root==nullptr ||root==p||root==q)return root; TreeNode *l=lowestCommonAncestor (root->left,p,q); TreeNode *r=lowestCommonAncestor (root->right,p,q); if (l==nullptr )return r; if (r==nullptr )return l; return root; } };
思路 事先存一个空节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseList (ListNode* head) { ListNode *pre=nullptr ; while (head!=nullptr ){ ListNode *curr=head->next; head->next=pre; pre=head; head=curr; } return pre; } };
思路 $O(2*n)$
找到left的前一个节点,left节点,right的后一个节点,right节点。对left到right这一段链表进行反转操作,然后再接回去。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseBetween (ListNode* head, int left, int right) { ListNode *dnode=new ListNode (-1 ); dnode->next=head; ListNode *pre=dnode; for (int i=0 ;i<left-1 ;i++){ pre=pre->next; } ListNode *l=pre; ListNode *r=pre; for (int i=0 ;i<right-left+1 ;i++){ r=r->next; } r=r->next; ListNode *st=pre->next; ListNode *ed=pre->next; ListNode *last=nullptr ; while (ed!=r){ ListNode *curr=ed->next; ed->next=last; last=ed; ed=curr; } l->next=last; st->next=r; return dnode->next; } };
$O(n)$
头插法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseBetween (ListNode* head, int left, int right) { ListNode *dnode=new ListNode (-1 ); dnode->next=head; ListNode *pre=dnode; for (int i = 0 ; i < left - 1 ; i++) { pre = pre->next; } ListNode *cur=pre->next; ListNode *next; for (int i=0 ;i<right-left;i++){ next=cur->next; cur->next=next->next; next->next=pre->next; pre->next=next; } return dnode->next; } };
思路
temp对应代码中的pre
node1对应head
node2对应nxt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public : ListNode* swapPairs (ListNode* head) { ListNode* dummy=new ListNode (-1 ); dummy->next=head; ListNode *pre=dummy; while (head!=nullptr ){ if (head->next==nullptr )break ; pre->next=head->next; ListNode *nxt=head->next; head->next=head->next->next; nxt->next=head; pre=head; head=head->next; } return dummy->next; } };
注意! 一开始写成了这样(没有新建nxt节点保存head->next),会进入死循环。因为head->next已经被更新为head->next->next了,所以head->next->next相当于是(head->next->next)->next
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 while (head!=nullptr ){ if (head->next==nullptr )break ; pre->next=head->next; head->next=head->next->next; head->next->next=head; pre=head; head=head->next; } retur
思路 先记录链表的总长度记为remain用92. 反转链表 II的头插法,每次头插k个,插完k个将pre置换成上一组翻转的最后一个,也就是cur,因为cur本来是第一个节点,一直被头插插到最后一个了。同时也要更新cur为pre->next
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution {public : ListNode* reverseKGroup (ListNode* head, int k) { ListNode* dummy=new ListNode (-1 ); dummy->next=head; ListNode* cntNode=head; int remain=0 ; while (cntNode!=nullptr ){ cntNode=cntNode->next; remain++; } ListNode *pre=dummy; ListNode *cur=head; ListNode *nxt; while (remain>=k){ int cnt=1 ; while (cnt<k){ nxt=cur->next; cur->next=nxt->next; nxt->next=cur; nxt->next=pre->next; pre->next=nxt; cnt++; } pre=cur; cur=pre->next; remain-=k; } return dummy->next; } };
思路 1.用一个map记录队列中数的情况,入队value,mp[value]++。出队q.front(),mp[q.front()]--,这里需要注意当mp[q.front()]为0时,要把mp.erase(q.front());
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class MaxQueue {public : queue<int >q; map<int ,int >mp; MaxQueue () { } int max_value () if (q.empty ())return -1 ; map<int ,int >::iterator it; it=mp.end (); it--; return it->first; } void push_back (int value) q.push (value); mp[value]++; } int pop_front () if (!q.empty ()){ int t=q.front (); mp[t]--; if (!mp[t])mp.erase (t); q.pop (); return t; } else { return -1 ; } } };
2.一个双端单调队列记录最大值,一个普通队列记录队列真实的出入顺序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class MaxQueue {public : queue<int >q; deque<int >d; MaxQueue () { } int max_value () if (q.empty ())return -1 ; else { return d.front (); } } void push_back (int value) while (!d.empty () && d.back () < value) { d.pop_back (); } d.push_back (value); q.push (value); } int pop_front () if (q.empty ())return -1 ; int t=q.front (); if (!d.empty ()&&d.front ()==t){ d.pop_front (); } q.pop (); return t; } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class CQueue {public : stack<int >s1,s2; CQueue () { } void appendTail (int value) s1.push (value); } int deleteHead () while (!s1.empty ()){ s2.push (s1.top ()); s1.pop (); } if (s2.empty ())return -1 ; int t=s2.top (); s2.pop (); while (!s2.empty ()){ s1.push (s2.top ()); s2.pop (); } return t; } };
思路 贪心
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public : int maxProfit (vector<int >& prices) int n=prices.size (); int minn=100005 ; int maxx=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ minn=min (minn,prices[i]); if (i>0 )maxx=max (maxx,prices[i]-minn); } return maxx; } };
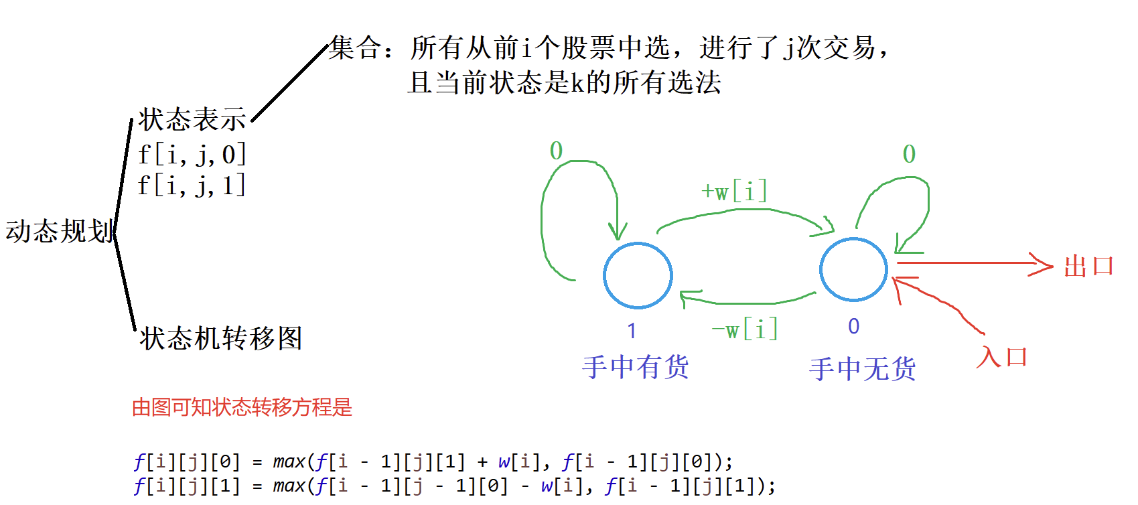
思路 状态机DP
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public : int maxProfit (vector<int >& prices) int dp[100005 ][2 ]; int n=prices.size (); dp[0 ][0 ]=0 ; dp[0 ][1 ]=-prices[0 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<n;i++){ dp[i][0 ]=max (dp[i-1 ][0 ],dp[i-1 ][1 ]+prices[i]); dp[i][1 ]=max (dp[i-1 ][1 ],dp[i-1 ][0 ]-prices[i]); } return max (dp[n-1 ][0 ],dp[n-1 ][1 ]); } };
思路 状态机DP
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public : int maxProfit (vector<int >& prices) int n=prices.size (); int dp[100005 ][5 ]; dp[0 ][0 ]=0 ; dp[0 ][1 ]=-prices[0 ]; dp[0 ][2 ]=dp[0 ][3 ]=dp[0 ][4 ]=-1e6 ; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ if (i>0 ){ dp[i][0 ]=dp[i-1 ][0 ]; dp[i][1 ]=max (dp[i-1 ][0 ]-prices[i],dp[i-1 ][1 ]); dp[i][2 ]=max (dp[i-1 ][1 ]+prices[i],dp[i-1 ][2 ]); dp[i][3 ]=max (dp[i-1 ][2 ]-prices[i],dp[i-1 ][3 ]); dp[i][4 ]=max (dp[i-1 ][3 ]+prices[i],dp[i-1 ][4 ]); } } int ans=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<5 ;i++){ ans=max (ans,dp[n-1 ][i]); } return ans; } };
思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public : int maxProfit (int k,vector<int >& prices) int dp[100005 ][105 ][2 ]; int n=prices.size (); memset (dp,-0x3f ,sizeof dp); for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i ++ ) dp[i][0 ][0 ] = 0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ for (int j=1 ;j<=k;j++){ dp[i][j][0 ]=max (dp[i-1 ][j][0 ],dp[i-1 ][j][1 ]+prices[i-1 ]); dp[i][j][1 ]=max (dp[i-1 ][j][1 ],dp[i-1 ][j-1 ][0 ]-prices[i-1 ]); } } int ans=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<=k;i++){ ans=max (ans,dp[n][i][0 ]); } return ans; } };
思路 unordered_map+双链表,主要复习stl的用法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class LRUCache {public : int cap; list<int >lis; unordered_map<int ,pair<int ,list<int >::iterator>>mp; LRUCache (int capacity) { cap=capacity; } int get (int key) auto it=mp.find (key); if (it==mp.end ())return -1 ; else { lis.erase (it->second.second); lis.push_back (key); mp[key].second=(--lis.end ()); return it->second.first; }; } void put (int key, int value) auto it=mp.find (key); if (it==mp.end ()){ if (mp.size ()>=cap){ int rmkey=lis.front (); lis.pop_front (); mp.erase (rmkey); } lis.push_back (key); mp[key]={value,--lis.end ()}; } else { lis.erase (it->second.second); lis.push_back (key); mp[key]={value,--lis.end ()}; } } };
思路 候选人(cand_num)初始化为 nums[0],票数 count 初始化为 1。cand_num 相同的数,则票数 count = count + 1,否则票数 count = count - 1。count 为 0 时,更换候选人,并将票数 count 重置为 1。cand_num 即为最终答案。
为何这行得通呢?票数 + 1,遇到不同的则 票数 - 1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public : int majorityElement (vector<int >& nums) int n=nums.size (); int cand_num=nums[0 ]; int cnt=1 ; for (auto i:nums){ if (i==cand_num)cnt++; else { cnt--; if (cnt==0 )cand_num=i,cnt=1 ; } } return cand_num; } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public : void rotate (vector<int >& nums, int k) int n=nums.size (); if (n==1 )return ; vector<int >curr; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++)curr.push_back (nums[i]); for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ nums[i]=curr[(i+n-k%n)%n]; } } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public : void rotate (vector<int >& nums, int k) int n=nums.size (); k=k%n; reverse (nums.begin (),nums.end ()); reverse (nums.begin (),nums.begin ()+k); reverse (nums.begin ()+k,nums.end ()); } };
思路 dp[i]意为以nums[i]这个数字结尾的最长上升子序列长度,所以转移方程考虑dp[i]=max(dp[k]+1) if nums[i]>nums[k] k=0...i-1
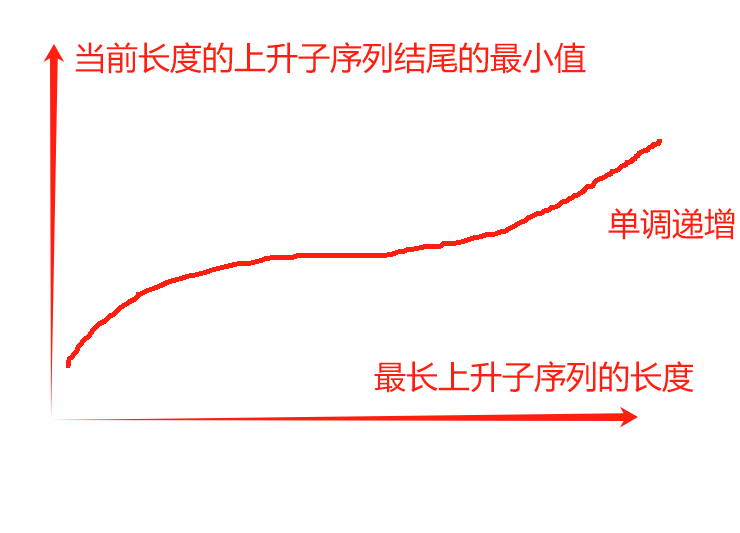
优化 对于每一个长度的上升子序列,只有结尾最小的是有用的。例如3 1 2 1 8 5 6,以3和1结尾的都是长度为1的最长上升子序列,但是1比3更好,所以3就没用了。
一个猜想:随着最长上升子序列长度的增加,不同长度的上升子序列的最小结尾也是单调递增的(反证法可得)
由上存储一个数组q[i](存的是所有长度为i的上升子序列的结尾最小值),假设一个数a,要求它的最长上升子序列,只需找到q中比它小的数中最大的数,假设为q[j],因为q[j]是小于a的最大的数,那么q[j+1]一定是大于等于a的,所以可以用a去更新q[j+1]
不懂就去看调试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {public : int lengthOfLIS (vector<int >& nums) int q[2505 ]; int n=nums.size (); q[0 ]=-2e4 ; int len=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ int l=0 ,r=len; int mid=0 ; while (l<r){ mid=(l+r+1 )/2 ; if (nums[i]>q[mid]){ l=mid; } else { r=mid-1 ; } } len=max (len,r+1 ); q[r+1 ]=nums[i]; } return len; } };
思路 主要展示优先队列自定义运算符较为简单的一种方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public : struct stru { int n; string id; bool operator <(const stru &a)const { if (a.n!=n)return a.n > n; else return a.id < id; } }; vector<string> topKFrequent (vector<string>& words, int k) { map<string, int >mp; for (auto i:words){ mp[i]++; } priority_queue<stru>heap; for (auto i:mp){ stru x={i.second,i.first}; heap.push (x); } vector<string>ans; while (!heap.empty ()){ auto top=heap.top (); ans.push_back (top.id); k--; if (!k)break ; heap.pop (); } return ans; } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 struct stru { int u, v, w; } edges[N]; bool cmp (stru a, stru b) return a.w < b.w; } sort (edges, edges + n - 1 , cmp);
思路 注意因为可以走回头路,所以不是DP,魔改dijkstra。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 class Solution {public :int dis[100005 ];bool st[100005 ];bool vis[105 ][105 ];vector<pair<int ,int >>g[100005 ]; bool judge (int i,int j, int c,int r) if (i<c&&i>=0 &&j<r&&j>=0 )return true ; else return false ; } int minimumEffortPath (vector<vector<int >>& heights) int dx[]={0 ,0 ,-1 ,1 }; int dy[]={1 ,-1 ,0 ,0 }; int r = heights[0 ].size (); int c = heights.size (); queue<pair<int ,int >>q; q.push ({0 ,0 }); while (!q.empty ()){ auto t=q.front (); q.pop (); if (vis[t.first][t.second])continue ; vis[t.first][t.second]=true ; int x,y; for (int i=0 ;i<4 ;i++){ x=t.first+dx[i],y=t.second+dy[i]; if (judge (x,y,c,r)&&!vis[x][y]){ int idx=t.first*r+t.second; int idx2=x*r+y; int di=abs (heights[t.first][t.second]-heights[x][y]); g[idx].push_back ({idx2,di}); g[idx2].push_back ({idx,di}); q.push ({x,y}); } } } dijkstra (); return dis[c*r-1 ]; } void dijkstra () priority_queue<pair<int ,int >, vector<pair<int ,int >>, greater<pair<int ,int >>> heap; memset (dis, 0x3f , sizeof dis); heap.push ({0 , 0 }); dis[0 ]=0 ; while (!heap.empty ()) { auto t = heap.top (); heap.pop (); int ver = t.second, distance = t.first; if (st[ver])continue ; st[ver] = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < g[ver].size (); i++) { auto j = g[ver][i]; if (dis[j.first] > max (distance , j.second)) { dis[j.first] = max (distance , j.second); heap.push ({dis[j.first], j.first}); } } } } };